
Understanding CSS Position Absolute for good!
In CSS, both relative and absolute position function differently. When you use relative and absolute positions in CSS, it opens a fresh world of design possibilities. Furthermore, this is a recap of our article about relative and absolute positions: Relative and absolute positions allow you to create visual elements in layers.
Position Relative And Absolute Difference In Css Design Talk
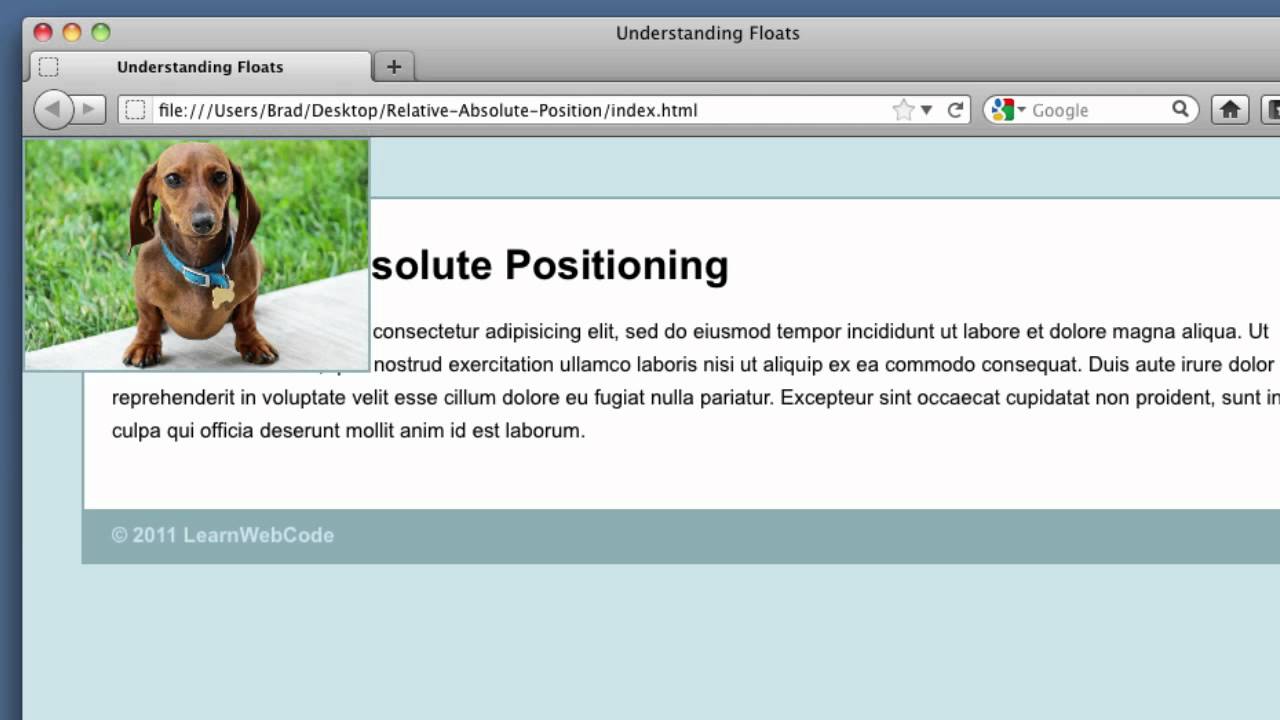
1 A relatively positioned element is positioned relative to its normal position. The absolutely positioned element is relative to the first parent container that has absolute or relative positioning. There is a great article here kolosek.com/css-position-relative-vs-position-absolute explaining the relative and absolute positions in detail.

Relative and Absolute Position CSS (with Examples)
In the example, the parent element has the position set to relative. Now, when you set the position of the child element to absolute, any additional positioning will be done relative to the parent.

CSS Position (relative,absolute,sticky,fixed) Detail lecture with examples YouTube
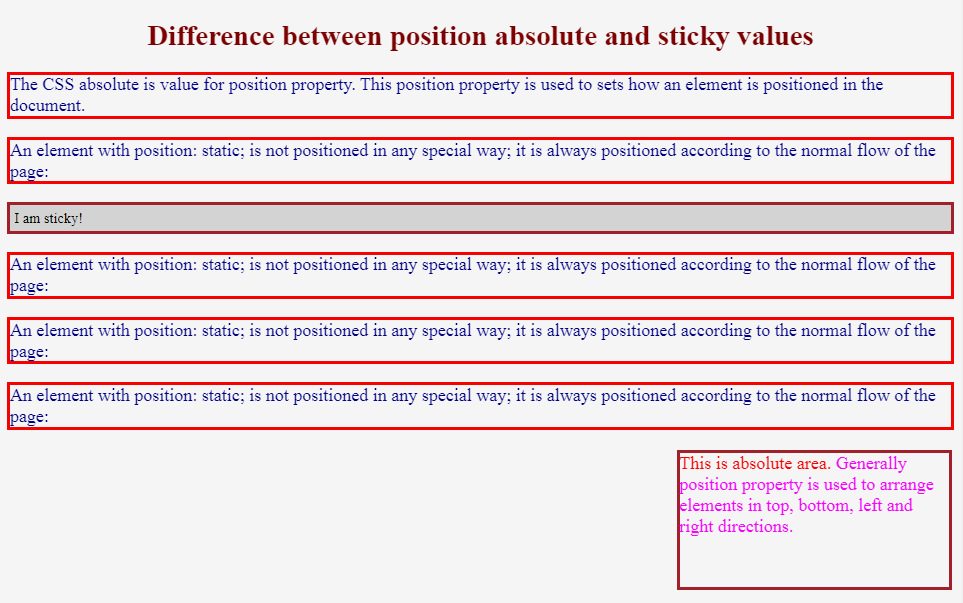
1. Static Position: static is the default value that an element will have. This means if you don't declare position for an element in CSS, it will automatically be set to static. It's important to note that having a static position is the same as not setting the position property at all.

Absolute vs Relative Positioning CSS Tutorial YouTube
What is the default position of HTML elements in CSS? By default, the position property for all HTML elements in CSS is set to static. This means that if you don't specify any other position value or if the position property is not declared explicitly, it'll be static.
CSS Absolute and Relative Positioning Tutorial YouTube
The difference between relative and absolute is that relative is "relative" to itself ( left:15px will pad it to the left with 15px), but absolute is relative to its parent (first non-static parent that is) and applying the same attribute (left:15px) will result in it being shifted 15px away form the left edge of the parent element.

Difference between css position absolute versus relative
Relative positioning moves an element with a particular document layout, while, on the other hand, absolute positioning moves an element from one document to another. The layout remains the same in the case of relative positioning, while on the other hand, absolute positioning changes the layout. The element remains within the normal document.

CSS Position Property Explained Static Relative Absolute Fixed CSS HTML Position YouTube
Difference between relative , absolute and fixed position in CSS Read Courses Relative Position: Setting the top, right, bottom, and left properties of an element with position: relative; property will cause it to adjust from its normal position. The other objects or elements will not fill the gap. Syntax: position: relative;

CSS Positions Static, Relative, Absolute, Fixed, Sticky, Zindex YouTube
CSS Position. CSS position is sometimes considered an advanced skill because it's not as intuitive as font-size or margin, etc., since it changes the natural "render flow" of the browser. These are the possible values for CSS position: .foo { position: static; /* position: relative; position: absolute; position: sticky; position: fixed.

【CSS】positionのrelativeとabsoluteの使い方と具体例を解説 ZeroPlus Media
absolute sticky Elements are then positioned using the top, bottom, left, and right properties. However, these properties will not work unless the position property is set first. They also work differently depending on the position value. position: static; HTML elements are positioned static by default.

css Difference between style = "positionabsolute" and style = "positionrelative" Stack
Watch on This is a brilliantly delivered CSS video tutorial! It breaks down the difference between absolute and relative positioning in a way that really makes sense for anyone getting started with CSS.

Absolute vs Relative positioning CSS Position Properties CSS Tutorial Adisma YouTube
absolute The element is removed from the normal document flow, and no space is created for the element in the page layout. The element is positioned relative to its closest positioned ancestor (if any) or to the initial containing block. Its final position is determined by the values of top, right, bottom, and left.

Absolute vs relative positioning CSS Tutorial With Live Preview CSS3 2017 Must Watch
The CSS position property defines the position of an element in a document. This property works with the left, right, top, bottom and z-index properties to determine the final position of an element on a page. There are five values the position property can take. They are: static relative absolute fixed sticky Let's discuss each one of them. Static

101 CSS Position Absolute vs Relative YouTube
The element is positioned based on the user's scroll position. A sticky element toggles between relative and fixed, depending on the scroll position. It is positioned relative until a given offset position is met in the viewport - then it "sticks" in place (like position:fixed). Note: Not supported in IE/Edge 15 or earlier.

CSS Relative vs Absolute Guide to These CSS Positioning Values
If you set position: relative; on an element but no other positioning attributes ( top, left, bottom or right ), it will have no effect on it's positioning at all, it will be exactly as it would be if you left it as position: static; But if you do give it some other positioning attribute, say, top: 10px;, it will shift its position 10 pixels dow.

Position Relative in CSS Difference in Relative and Absolute 6 YouTube
Both the relative position and absolute position work in the same way except in one field. We use relative to identify the parent class. And we use absolute to identify the children classes. Position VS relative position Let's look at 2 examples 👇. First, let's experiment with the relative value. Try out this code:.box-1{ /* Other codes are.